The Role of a Hydration Nurse: Understanding the Responsibilities of a Vital Healthcare Position
In hospitals and healthcare facilities across the country, there is a vital role that often goes unnoticed: the hydration nurse. These specialized nurses play a crucial role in ensuring that patients are properly hydrated and receiving the necessary fluids and electrolytes for optimal health. In this article, we'll take a closer look at the responsibilities, training, and essential skills required for this important healthcare position.

What is a Hydration Nurse?
Definition and Overview
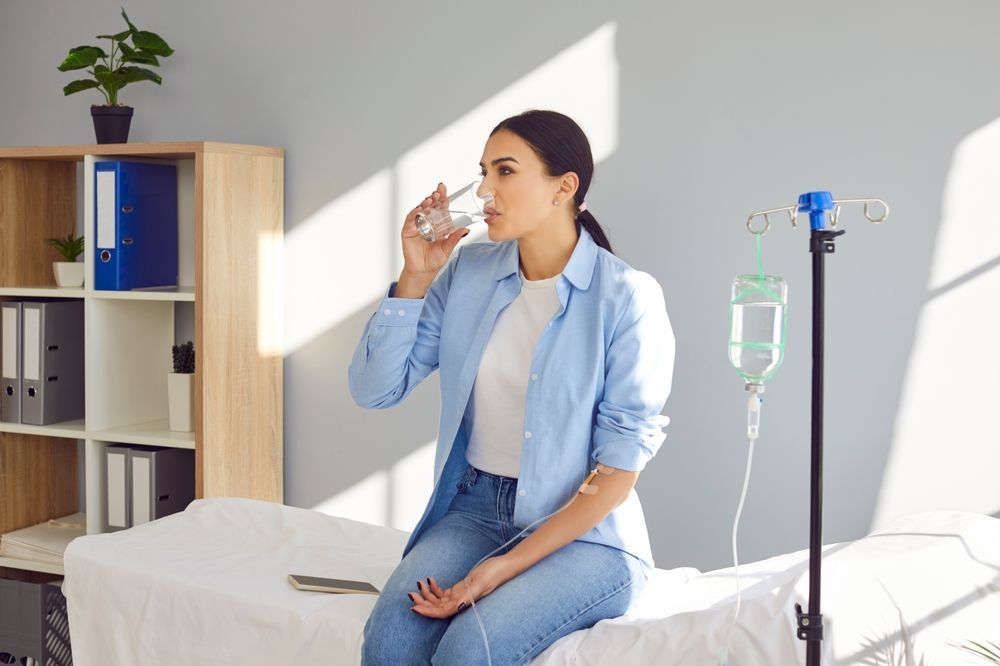
A hydration nurse is a registered nurse who specializes in the management of intravenous (IV) therapy and ensuring that patients are receiving the appropriate fluids for their individual needs. These nurses play a vital role in a patient's overall health and recovery, promoting proper hydration to prevent complications and improve outcomes.
The Importance of Hydration in Patient Care
Proper hydration is essential for the body to function properly, but patients who are ill or recovering may need additional fluids and electrolytes to promote healing. Patients who are dehydrated may experience a range of symptoms, including weakness, confusion, and a weakened immune system. Hydration nurses are responsible for ensuring that patients are receiving the appropriate fluids to prevent these symptoms from occurring.
Hydration nurses work closely with physicians, other nurses, and healthcare professionals to develop individualized hydration plans for each patient. These plans take into account the patient's medical history, current condition, and any medications they may be taking that could affect their fluid balance.
In addition to administering IV fluids, hydration nurses also monitor patients for signs of dehydration or fluid overload. They may adjust the rate of fluid administration or the type of fluids being given based on the patient's response to treatment.
The Role of Hydration Nurses in Preventing Complications
Hydration nurses play a critical role in preventing complications related to dehydration or fluid overload. For example, patients who are receiving chemotherapy or radiation therapy may experience nausea and vomiting, which can lead to dehydration. Hydration nurses can administer fluids and electrolytes to help prevent dehydration and promote healing.
Similarly, patients who are recovering from surgery may be at risk for fluid overload if they are unable to eliminate fluids as quickly as they are being administered. Hydration nurses can monitor these patients closely and adjust their fluid intake as needed to prevent complications.
The Future of Hydration Nursing
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the role of hydration nurses is becoming increasingly important. With an aging population and an increase in chronic diseases, the demand for skilled hydration nurses is expected to grow in the coming years.
In addition, advances in technology are making it easier for hydration nurses to monitor patients remotely and adjust their treatment plans as needed. This means that patients can receive the care they need from the comfort of their own homes, reducing the need for hospitalization and improving outcomes.
Overall, hydration nurses play a vital role in promoting proper hydration and preventing complications in patients. Their expertise and dedication are essential to improving patient outcomes and ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
Educational Requirements and Training
Becoming a hydration nurse requires a significant amount of education and training. Not only must individuals obtain a degree in nursing and become a registered nurse, but they must also receive specialized certification in IV therapy and hydration management.
Necessary Degrees and Certifications
As mentioned, the first step in becoming a hydration nurse is to obtain a degree in nursing and become a registered nurse. This typically requires completing a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) program or an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) program and passing the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX-RN).
However, to work as a hydration nurse, most employers also require specialized certification in IV therapy. The most common certifications for hydration nurses include the CRNI (Certified Registered Nurse Infusion) and the VA-BC (Vascular Access-Board Certification).
These certifications demonstrate that the nurse has received specialized training in IV therapy and is qualified to administer and manage intravenous fluids.
Specialized Training and Continuing Education
While obtaining the necessary degrees and certifications is important, it is also essential for hydration nurses to receive specialized training in IV therapy and hydration management.
Many hospitals and healthcare facilities offer specialized courses and training programs to provide this education. These programs may cover topics such as:>
- The anatomy and physiology of the circulatory system
- The different types of IV fluids and their uses
- The proper techniques for inserting and removing IV catheters
- The signs and symptoms of fluid and electrolyte imbalances
- The best practices for monitoring and managing hydration levels
Additionally, hydration nurses are required to remain up-to-date on the latest developments and best practices in hydration management to provide the best care possible to their patients.
This may involve attending continuing education courses, reading industry publications, and participating in professional organizations and conferences.
Overall, becoming a hydration nurse requires a significant amount of education and training. However, the reward of helping patients maintain optimal hydration levels and improve their overall health and well-being makes it all worthwhile.
Key Responsibilities of a Hydration Nurse
Hydration nurses are essential members of the healthcare team, responsible for ensuring that patients receive the fluids and electrolytes they need to maintain optimal health and well-being. In addition to assessing patients' hydration needs and developing tailored hydration plans, hydration nurses also monitor treatment effectiveness and educate patients and families on the importance of proper hydration.
Assessing Patient Hydration Needs
Assessing a patient's hydration needs is the first and most crucial responsibility of a hydration nurse. This involves evaluating the patient's medical history and current condition, as well as monitoring their fluid intake and output. Hydration nurses must be skilled at recognizing the signs and symptoms of dehydration, such as dry mouth, decreased urine output, and dark urine, in order to intervene promptly and prevent further complications.
Hydration nurses also consider other factors that can impact a patient's hydration needs, such as age, weight, medications, and medical conditions. For example, elderly patients may be at higher risk for dehydration due to decreased thirst sensation, while patients with kidney disease may require special attention to avoid electrolyte imbalances.
Developing and Implementing Hydration Plans
Based on their assessment of a patient's hydration needs, hydration nurses develop and implement hydration plans that are tailored to each patient's individual needs. These plans may include oral fluids, IV therapy, or a combination of both. Hydration nurses must also ensure that patients are receiving all necessary fluids and electrolytes to prevent dehydration and promote health and healing.
Hydration plans may vary depending on the patient's condition and treatment goals. For example, patients undergoing surgery may require IV fluids to maintain hydration during the procedure, while patients with chronic conditions such as heart failure may require ongoing monitoring and adjustment of their hydration plan.
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment as Needed
Hydration nurses must monitor patients closely to ensure that their hydration plans are effective and adjust treatment as needed. This may involve modifying the type or amount of fluids, altering the rate of infusion, or making other adjustments to promote optimal hydration and health.
Hydration nurses also monitor for potential complications of hydration therapy, such as fluid overload or electrolyte imbalances. They must be skilled at recognizing the signs and symptoms of these complications and taking appropriate action to prevent further harm.

Educating Patients and Families on Hydration Management
Hydration nurses also play an important role in educating patients and their families on hydration management and the importance of proper hydration. This may include discussing the benefits of staying properly hydrated, providing education on hydration management following discharge, and answering any questions that patients and their families may have.
<p>Hydration nurses may also provide guidance on lifestyle factors that can impact hydration, such as diet and exercise. They may work with patients to develop strategies for increasing fluid intake, such as setting reminders to drink water or incorporating hydrating foods into meals.
Overall, hydration nurses are essential members of the healthcare team, responsible for ensuring that patients receive the fluids and electrolytes they need to maintain optimal health and well-being. Through careful assessment, tailored hydration plans, and ongoing monitoring and education, hydration nurses help patients stay hydrated and healthy.
Skills and Qualities of a Successful Hydration Nurse
Hydration is a critical aspect of patient care, and a successful hydration nurse must possess a combination of clinical knowledge, communication skills, attention to detail, and adaptability to provide the best care possible to their patients.
Clinical Knowledge and Expertise
Hydration nurses must have a strong understanding of the human body and how it functions, particularly in relation to fluid and electrolyte balance. They must also have expertise in hydration management and IV therapy, including the different types of IV fluids and how to administer them safely and effectively. In addition, successful hydration nurses must stay up-to-date on the latest developments and best practices in hydration management to provide the most current and effective care to their patients.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills
Effective communication is essential for hydration nurses, as they must be able to communicate effectively with patients, their families, and other healthcare providers. They must be able to explain complex medical concepts in a way that patients and families can understand, as well as listen actively to their concerns and questions. In addition, successful hydration nurses must possess strong interpersonal skills and be able to connect with patients on a personal level to promote trust and overall well-being.
Attention to Detail and Organization
Attention to detail and organization are critical skills for hydration nurses, as they must ensure that patients are receiving the appropriate fluids and electrolytes for their individual needs. They must be able to accurately calculate and measure fluid intake and output, monitor vital signs, and adjust treatment plans as needed. In addition, successful hydration nurses must be able to document patient progress and treatment plans accurately and efficiently.
Adaptability and Problem Solving
Finally, successful hydration nurses must be adaptable and skilled at problem-solving. They must be able to quickly assess new situations and adjust treatment plans as needed to promote optimal hydration and overall health. They must also be able to troubleshoot any issues that arise with IV therapy, such as catheter blockages or infiltration, and take appropriate action to prevent complications.
In conclusion, a successful hydration nurse must possess a combination of clinical knowledge, communication skills, attention to detail, and adaptability to provide the best care possible to their patients. By staying up-to-date on the latest developments and best practices in hydration management and IV therapy, and by connecting with patients on a personal level, hydration nurses can make a significant difference in the health and well-being of their patients.
Conclusion
Hydration nurses play a vital role in ensuring that patients are properly hydrated and receiving the fluids and electrolytes needed for optimal health. These specialized nurses must possess a range of skills and qualities, including clinical knowledge, communication skills, attention to detail, and problem-solving abilities. As the importance of proper hydration in patient care continues to be recognized, the role of the hydration nurse will only become more essential to the healthcare industry.